
When we log in to our Mac, in addition to the administrator or standard user account that we can have configured in our user, depending on what it is taress for, OS X has other types of accounts with different privileges and permissions, which remain hidden or transparent to the user, however they are absolutely necessary for run tasks and processes that remain active in the background so that the system can function normally.
These tasks are executed most of them under the broken account, which allows to have unlimited access to all system functions globally, so it can result in a security breach if we do not use it for very specific tasks since there will be no pop-up windows warning us of changes in the system, it will not even alert us with a credential identification.
Apple even warns us of the danger that may entail,
The root user should only be used for specific administration and monitoring tasks. After finishing a task as root user, you must log out of Mac OS X and log in again using a normal or administrator account. You should disable root access if you don't use it often.
We previously talked about how to activate it in Snow Leopard with this little guide, but if it were the case that it could not be accessed or had a problem, we can do it in two different ways:
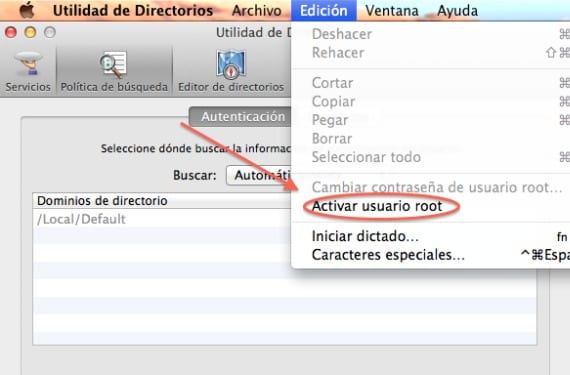
- Directory utility: The «Directory utility» is a tool that is not exactly accessible and remains semi-hidden in this path »/ System / Library / CoreServices«, and there we will find the directory utility to activate it in edition - Activate root user.
- Terminal: By using the terminal we will be able to access as root in a much simpler way than through the Directory Utility, we will simply have to write the following command dsenableroot.
More information - Tip: Activate the Root user in Snow Leopard